“First-class Medical Staff & comprehensive System”
Siloam Eye Hospital will Safeguard your Health.

What is CATARACT?
A ‘cataract’ refers to the lens of one’s eyes becoming cloudy, causing the perception of objects to become blurred. This lens, positioned behind the iris (colored part of one’s eye), focuses light to produce a clear image on the retina.
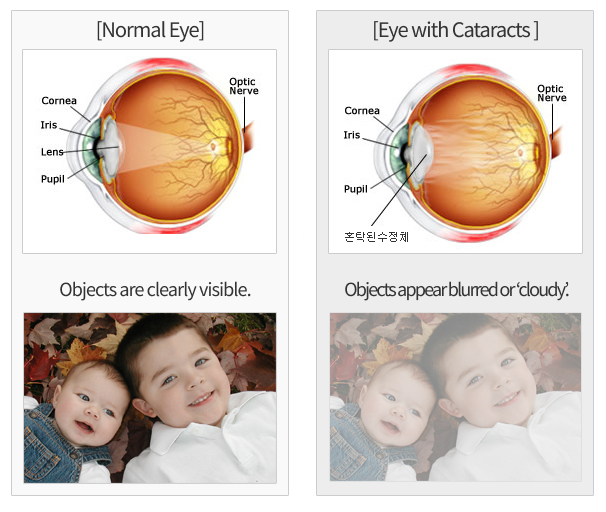
Cataract are caused by a variety of factors—aging, the result of trauma, inflammation of the uvea, diabetes, or complications stemming from congenital or ophthalmic diseases. Senile Cataract (Age-Related Cataract) is the most common, which begin forming in nearly every over the age of 50 due senescence, the natural aging process.
Most people experience a gradual loss of vision without any serious side effects. However, painful and serious symptoms may be experienced if other abnormalities like glaucoma occur compounding the problem of cataract. In the case of cataract resulting from trauma or other complications due to disease, vision loss may progress quite rapidly.
Although eye drops and other medications are often prescribed to treat cataract, the underlying problem can not be ‘cured’ using these methods. Once cataract have advanced to a certain stage, the only treatment available is surgery.
Cataract Symptoms
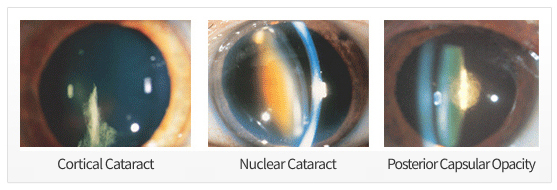
The initial opacity around the lens caused by cataract usually does not result in much visual impairment—although this may depend on the the cataract location, degree, and type of opacity caused. However, if cataract form in the pupil or posterior pole, it can cause extreme sensitivity to and discomfort in bright light (day blindness), and it can lead to poor near-sighted vision. On the other hand, one’s vision may improve in dark places or when the pupils are dilated. As a cataract progresses and one’s vision increasingly becomes cloudier, this will always result in loss of vision.
If there is partial opacity, there are two objects when viewed with one eye. Visible symptoms may also occur (single-eye double vision). If the lens nucleus hardens and the refractive power increases, the eyes become myopic, and a person who used to wear magnifying glasses may see well near text without glasses (lens myopia). Other symptoms include loss of color vision and polycythemia.
Causes of Cataract
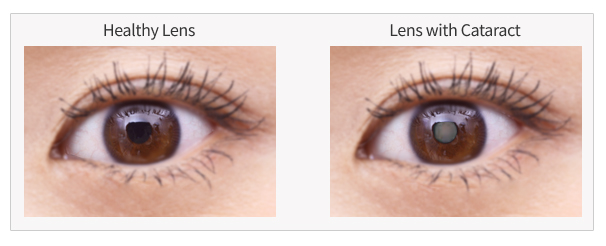
Senile Cataract is the most common type of cataract that occurs due to aging of the eyes. Senile Cataract naturally develop in 70% of people in their 60s, 90% of people in their 70s, and almost 100% of people over 80 years of age—and can decrease one’s vision. For younger people, the cause is often eye trauma, atopic dermatitis, diabetes, or malnutrition.
Other factors that can cause cataract are: genetics, X-rays infra-red radiation, and steroids or psychotropic drugs. Additionally secondary cataract (reappearance after cataract extraction) can be caused by retinal detachment or vitreous surgery, glaucoma surgery, or eye diseases such as uveitis. Congenital cataract are also a rare condition where a baby is born with his or her lens being cloudy at birth.
Cataract Surgery Guide
As long as there are no special complications, the decision for surgery is made taking into account the disease’s progress and visual acuity. In general, if you feel discomfort in your daily life due to poor vision, it is the time to have surgery.
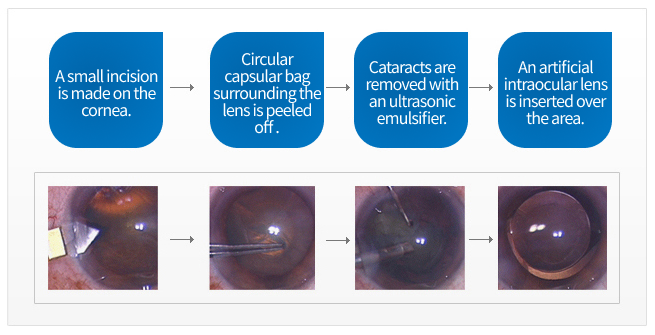
Process of Ultrasound Cataract Surgery